Alcohol Awareness: Understanding the Risks
Let's talk about alcohol. You might not know this, but it's classified as a poison. And it's not just any poison; it's a dangerous one that can be deadly.
So, what exactly does alcohol do to your body? Well, first off, it's a Central Nervous System depressant. This means that as soon as you take even one sip, it starts messing with your nervous system. It kicks off by messing with your brain – you know, the part that helps you make smart decisions and control your feelings.
But that's not all. Did you know alcohol is also flammable? Imagine that – something you drink catching fire!
Sure, alcohol might be a common sight at parties and get-togethers, but here's the thing – drinking and driving? Big no-no. When you're under the influence, your driving skills take a serious hit. You're more likely to zone out instead of paying attention to the road. And forget about multitasking – it's just not happening. But when you're driving, you need to be on your A-game, handling multiple things at once to stay safe.
And even a tiny bit of alcohol can mess with your vision and judgment. Imagine driving at night with fuzzy vision and slow reactions – not a good combo.
Speaking of crashes, alcohol messes with your brain's ability to spot hazards and react quickly. So, if you find yourself in a sticky situation on the road, you might not be able to think fast enough to get out of it.
Bottom line? Alcohol and driving just don't mix. It messes with your head, slows you down, and puts everyone on the road at risk. So, next time you're tempted to drink and drive, think twice – because your life and the lives of others are worth way more than a few sips of alcohol.
Here is a powerful, short video about WHY you don't want to drink and drive!
Take a look at this chart showing how many drinks it takes to impair driving ability.
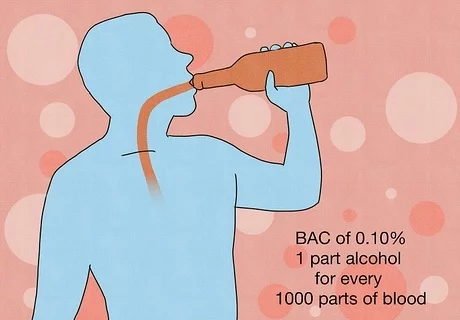
Understanding Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC)
Your Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) is the measure of alcohol in your bloodstream, defining your level of intoxication. Several factors influence your BAC:
In California, a BAC of 0.08% indicates legal intoxication for individuals over 21. To put it in perspective, this means you have 8/10ths of a drop of alcohol for every 1,000 drops of blood in your body!
For those under 21, impairment is noted at 0.01%. Despite feeling euphoric or happy due to alcohol's effect on the brain's "pleasure center," your motor skills may be significantly impaired, making activities like driving unsafe.
Here's a breakdown of BAC levels and associated effects:
Consuming 12 drinks can elevate BAC levels to 0.50%, a dangerously high level potentially leading to death.
It's important to note that regardless of the source (beer, wine, or spirits), the amount of alcohol in standard servings remains consistent. Upon ingestion, alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream and metabolized by the liver, with a processing rate of approximately one ounce of liquor per hour.
Contrary to common myths, sobering up isn't hastened by cold showers, coffee, or exercise. The sobering process depends on factors such as body weight and food intake, with no reliable methods for expediting it.
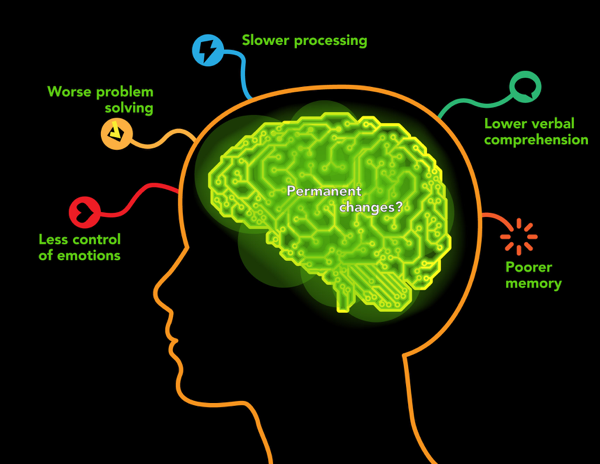
Understanding Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) and its Impact on the Brain
Alcohol's effects on the brain are profound, as it traverses through three key regions:
Understanding how alcohol impacts these crucial areas of the brain sheds light on its cognitive and physical effects, emphasizing the importance of responsible consumption and the avoidance of activities like driving while under its influence.
Understanding Drinking and Gender Differences
When it comes to processing alcohol, gender plays a significant role due to differences in physiology:
Ability to Dilute Alcohol: Females generally have a lower percentage of body water compared to males. This means they're less able to dilute alcohol swiftly. Consequently, women tend to experience the effects of alcohol more rapidly and intensely than men, even with the same amount consumed.
Average Total Body Water:
Ability to Metabolize Alcohol: Alcohol metabolism relies on enzymes like dehydrogenase, which convert alcohol molecules into other compounds utilized by the body. Women typically have lower levels of dehydrogenase compared to men. As a result, their bodies process alcohol at a slower rate.
Understanding these gender-based differences underscores the importance of responsible alcohol consumption and highlights why it's crucial to consider individual factors, such as gender, when assessing one's tolerance and potential effects of alcohol.
Take a look at this chart showing alcohol-impaired drivers involved in fatal crashes.
Understanding DUI and Alcohol-Related Penalties
DUI, or "driving under the influence," encompasses being impaired by prescription, non-prescription, or illegal drugs, in addition to alcohol.
For individuals aged 21 and above, the legal threshold for DUI is a Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) of 0.08% or higher. However, if operating a commercial vehicle, the limit is reduced to 0.04% or greater. It's important to note that DUI convictions can occur at any BAC level if signs of impairment are present.
Studies indicate that even at a BAC level as low as 0.05%, driving abilities may be compromised. Moreover, individuals under 21 face penalties under zero tolerance laws for driving with a BAC of 0.01% or higher.
Upon arrest on suspicion of DUI, drivers implicitly consent to alcohol or drug testing. Refusal to comply can result in suspension or revocation of the driver's license, alongside potential DUI convictions.
Under Administrative Per Se (Admin Per Se) laws, individuals aged 21 and above driving with a BAC of 0.08% or higher, and those under 21 with a BAC of 0.01% or greater, face automatic suspension or revocation of their driving privileges. This administrative action is distinct from criminal proceedings and can take effect independently.
Immediate license suspension or revocation occurs at the time of arrest. For a first offense, suspension lasts 120 days, extending to one year for individuals with prior alcohol-related offenses.
Understanding the legal implications of DUI and alcohol-related offenses underscores the importance of responsible driving behavior and adherence to traffic laws.
Understanding DUI Regulations and Penalties
When it comes to driving under the influence (DUI), strict regulations are in place to ensure public safety:
DUI penalties can be severe, including:
For first-time offenders, additional requirements may include attendance at alcohol treatment programs and filing proof of insurance with the Department of Motor Vehicles.
Understanding the consequences of DUI emphasizes the importance of responsible driving behavior and the severe penalties associated with violating DUI laws.
Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Driving
Many of the same principles that apply to alcohol also extend to drugs, whether they are legally prescribed medications or illegal substances. California's DUI law encompasses "driving under the influence of alcohol and/or drugs," emphasizing the seriousness of impaired driving regardless of the substance involved.
Driving under the influence of any drug, whether legally prescribed, over-the-counter, or illicit, that impairs driving ability is illegal. Virtually any drug has the potential to affect a person's driving skills, making it crucial to understand the effects of any medication before getting behind the wheel.
Individuals convicted of possessing, selling, or manufacturing illegal drugs face a six-month suspension of their driving privilege under California law.
When taking new medications, it's essential to be aware of how they interact with alcohol. Some medications may slow the body's processing of alcohol, increasing the risk of impairment even with fewer drinks than usual. It is the responsibility of the individual to know the effects of any medication they take, particularly those that warn of potential drowsiness or dizziness, as these can significantly impact driving ability.
The fact that a drug is available over the counter does not diminish its potential dangers or the illegality of driving under its influence. Various over-the-counter medications, including painkillers, sleeping aids, diet pills, tranquilizers, allergy medications, and cough suppressants, can impair driving ability.
Additionally, some medications, such as cough syrup, may contain alcohol, while energy pills, "uppers," and diet pills can initially increase alertness but later cause nervousness, dizziness, and concentration difficulties, negatively affecting vision and driving performance.
Over-the-counter cold and allergy medicines can induce drowsiness and impair driving ability. It's crucial to carefully read and follow dosage instructions and heed warnings about continued use and who should avoid driving after taking the medication.
Understanding the potential effects of drugs on driving is essential for ensuring road safety and complying with California laws regarding impaired driving.
Understanding the Effects of Drugs on Driving (Continued)
The fact that a drug is prescribed by a doctor doesn't diminish its potential dangers or the illegality of driving under its influence. Narcotics like codeine and Demerol, as well as other painkillers, can induce drowsiness, a stupor-like condition, a false sense of well-being, and poor coordination, significantly impairing driving ability.
It's crucial never to mix medications unless directed by a physician, and medications prescribed for someone else should never be taken. Driving while impaired by any amount of illegal drugs can lead to DUI conviction, as there is no legally acceptable level of drug use while driving, similar to alcohol.
For individuals under 21 but older than 13, a drug-related offense conviction can result in a one-year suspension of driving privileges. Depressants such as sleeping pills, tranquilizers, and barbiturates can cause drowsiness, inability to stay awake, slowed reactions, and poor coordination, posing significant dangers when driving.
Stimulants like methamphetamine, crack, and cocaine can lead to a false sense of well-being, difficulty in concentrating, aggressiveness, chronic paranoia, and impatience, further compromising driving abilities.
Marijuana's effects on driving encompass reduced alertness, impaired concentration, coordination, and reaction time. These effects can persist for up to 24 hours after use, making it challenging to judge distances and react to road signals and sounds. Combining marijuana with alcohol can exacerbate driving hazards beyond the effects of either drug alone.
Understanding the profound impact of drugs on driving skills underscores the importance of abstaining from drug use before operating a vehicle and the serious legal consequences associated with driving under the influence of drugs in California.
Understanding the Effects of Narcotics and Hallucinogens on Driving
Narcotics can severely impact driving abilities by:
Drivers impaired by narcotics find it challenging to make quick decisions in evolving traffic situations, posing significant risks on the road.
Hallucinogens such as LSD, mescaline, PCP, and peyote can cause hallucinations affecting vision, hearing, or touch. These hallucinations distort perception, making it difficult to detect hazards and impairing judgment. Additionally, these drugs can induce feelings of super strength, invulnerability, and aggressive behavior, further jeopardizing road safety.
Combining illegal, prescription, or over-the-counter drugs with other substances like alcohol can exacerbate impairments, significantly affecting vision, judgment, and reaction time beyond what would be expected from taking the drugs individually.
Understanding the profound effects of narcotics and hallucinogens on driving underscores the importance of refraining from drug use before driving and highlights the severe consequences associated with impaired driving in California.
Avoiding impaired driving is crucial for ensuring road safety. Here are some strategies to help you stay safe:
The designated driver program aims to have one individual in a group abstain from alcohol consumption to safely drive others home. Many establishments support this initiative by offering complimentary nonalcoholic beverages to the designated driver.
To serve as a designated driver:
Recognizing signs of intoxication while driving is essential. Intoxicated drivers may exhibit behaviors such as driving at erratic speeds, making frequent lane changes, ignoring traffic signs, and weaving between lanes. If you suspect an impaired driver, maintain a safe distance, consider pulling over, and alert law enforcement using community hotlines dedicated to reporting drunk driving incidents.
By taking proactive measures and staying vigilant on the road, we can collectively work towards preventing impaired driving and ensuring the safety of all road users.
You have reached the last page for this lesson. Each lesson is marked completed when you answer all Quiz questions correctly.
Upon completing all lessons, you'll find a "Take Test" button at the bottom of the lesson list. Select it to access the final test. To pass, you'll need a score of 80% or better. You can retake the final test as many times as needed to pass.
When you pass the final test:
This ensures a smooth process and allows users to proceed confidently with their driver education. If you have any questions or concerns, feel free to contact us for assistance.
You will now answer 5 questions to test what you learned during this lesson. You must answer all questions correctly to receive completion credit for this lesson. You may answer the questions as many times as necessary to get them right.
You should review the lesson material if you don't do well on the quiz.
 Download DMV Publications
California Parent-Teen Training Guide
California Driver Handbook & DMV Publications
Download DMV Publications
California Parent-Teen Training Guide
California Driver Handbook & DMV Publications
*Check with your California insurance agent for eligibility details. Every licensed California Driver must have auto insurance to drive a vehicle in California. Proof of insurance must be provided to the California DMV when you obtain your drivers license (not your learners permit).